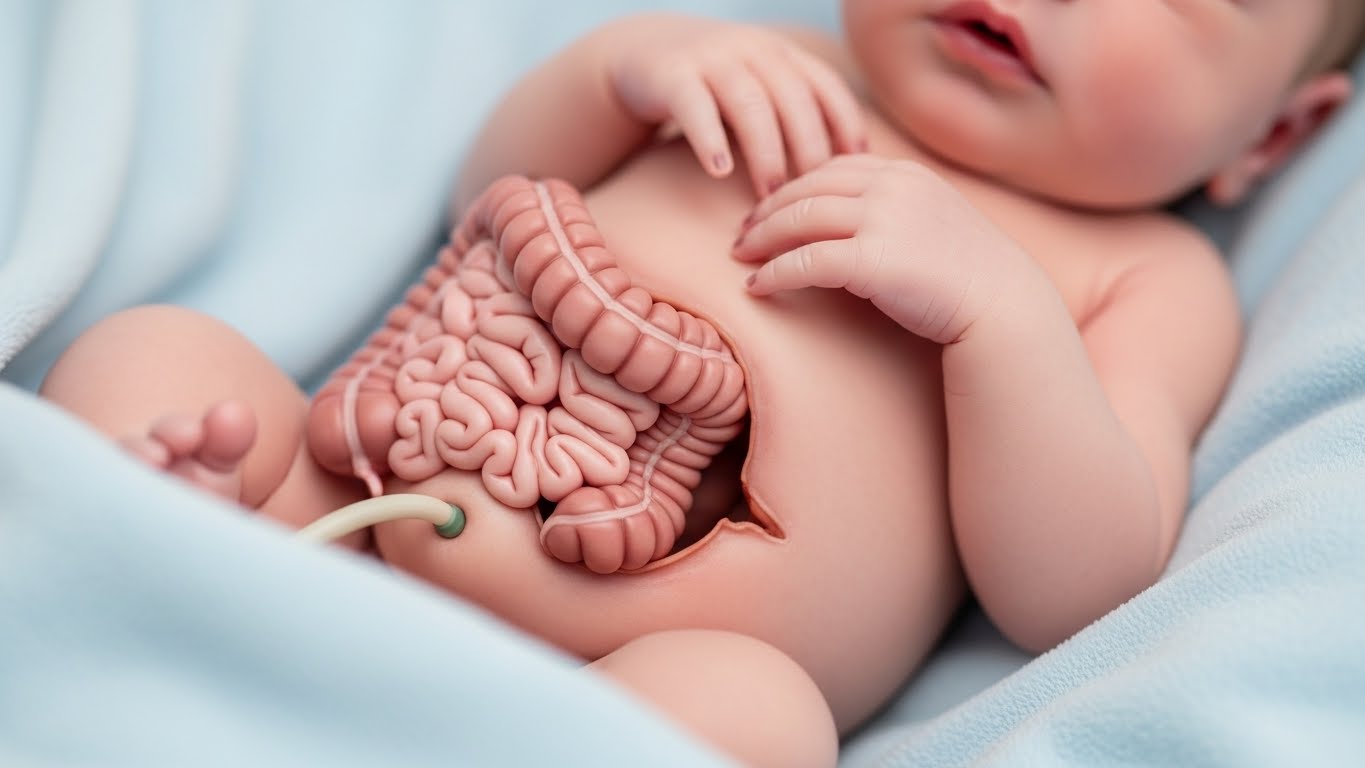
Gastroshiza is a term that may not be familiar to many, yet it represents a significant challenge for some families. This birth defect, characterized by the protrusion of intestines outside the body, can bring about overwhelming feelings of uncertainty and concern. While it might sound alarming, understanding gastroshiza is crucial for parents preparing to welcome a child with this condition.
As we delve deeper into what gastroshiza entails—its causes, symptoms, and treatment options—you’ll gain valuable insights into how families navigate this journey. Whether you’re seeking information for yourself or supporting someone close to you, knowledge can empower you in facing the challenges ahead. Let’s explore the world of gastroshiza together and shed light on available resources that can make a difference.
What is Gastroshiza?
Gastroshiza is a congenital condition that affects newborns, marked by the intestines protruding through an opening in the abdominal wall. This defect typically occurs to the right of the umbilical cord and can vary in severity.
The exposed intestines are often vulnerable, making immediate medical attention crucial after birth. This condition usually develops early in pregnancy during fetal development when the abdominal wall fails to close properly.
Unlike some other similar conditions, gastroshiza does not involve any protective sac around the protruded organs. This unique aspect adds complexity to treatment and management strategies post-delivery.
Understanding gastroshiza helps caregivers better prepare for potential challenges ahead. With advancements in medical care, many children with this condition grow up healthy under proper supervision and treatment protocols.
Causes and Risk Factors
Gastroshiza occurs when a baby’s intestines protrude through a defect in the abdominal wall. The exact causes remain unclear, but several factors may increase the risk.
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role. If there is a family history of gastrointestinal defects, the likelihood of gastroshiza may rise.
Environmental influences are also considered. Exposure to certain medications or harmful substances during pregnancy could contribute to this condition.
Maternal health is another crucial factor. Women who smoke, use drugs, or have diabetes may see higher instances of gastroshiza in their babies.
Age can impact risk as well; younger mothers are often at higher risk for complications leading to this birth defect. Understanding these elements helps parents take proactive steps while expecting.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Gastroshiza is often detected during routine prenatal ultrasounds. Healthcare providers look for the characteristic protrusion of intestines outside the abdominal wall.
Symptoms may vary based on severity. In infants, visible intestinal loops can be seen at birth. These loops are usually covered only by a thin membrane, making them vulnerable.
Parents might notice other signs like difficulty feeding or abnormal bowel function shortly after delivery. Swelling in the abdomen could also occur as fluid accumulates.
A timely diagnosis is crucial for proper treatment planning. Doctors typically perform imaging studies to assess the condition further and determine any associated anomalies that may exist alongside gastroshiza.
Early intervention plays a vital role in ensuring better outcomes for affected children. Identifying this defect early allows families to prepare emotionally and medically for their newborn’s journey ahead.
Treatment Options
Treatment for gastroshiza primarily involves surgical intervention shortly after birth. The procedure aims to return the protruding intestines back into the abdominal cavity.
Surgeons may perform a primary closure if conditions permit. This means stitching up the abdomen in one go, allowing for a quicker recovery. However, in some cases, a staged approach is necessary.
For infants with significant intestinal damage or complications, additional surgeries might be required. These can include bowel resections or using synthetic materials to form an artificial abdominal wall.
Post-surgery care plays a crucial role in recovery. Monitoring nutrition and growth becomes essential as children adjust to their new digestive dynamics.
Families should work closely with pediatric specialists throughout this journey. Early interventions and consistent follow-ups help ensure the best outcomes for affected children.
Long-Term Effects on Children and Families
Gastroshiza can have lasting impacts on children and their families. The physical challenges often extend beyond the immediate medical attention required at birth. Many children face ongoing health issues, including feeding difficulties and potential growth delays.
Emotional adjustments are also common within families. Parents may experience anxiety about their child’s development and future health. Siblings might feel overlooked as the family navigates frequent hospital visits or treatments.
Social interactions can be affected too. Children with gastroshiza may have unique needs that set them apart from peers, influencing their self-esteem and social skills.
Support systems become essential for both parents and siblings to cope with these changes effectively. Establishing a strong network helps families manage challenges while fostering resilience in children facing this condition.
Coping Strategies for Parents and Caregivers
Navigating the journey of raising a child with gastroshiza can be overwhelming. Building a support network is essential. Connect with other parents who understand your experience. Sharing stories and resources can lighten the emotional load.
Educate yourself about gastroshiza to make informed decisions regarding your child’s care. Knowledge empowers you and helps dispel myths that may arise from misunderstandings.
Practice self-care regularly. It’s easy to become consumed by worry, but taking time for yourself rejuvenates both body and mind. Consider activities like meditation or light exercise to manage stress effectively.
Establish routine in daily life; this brings a sense of normalcy amid uncertainty. Involve siblings in age-appropriate discussions about their brother or sister’s condition, fostering understanding within the family unit.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if needed—therapists specializing in pediatric conditions can provide valuable coping techniques tailored just for you.
Research and Advancements in Treatment
Research into gastroshiza has made significant strides in recent years. Scientists are exploring various surgical techniques to improve outcomes for affected infants. Minimally invasive procedures show promise, reducing recovery time and complications.
New imaging technologies also play a crucial role. Advanced ultrasound methods allow for earlier diagnosis, enabling timely intervention. This proactive approach can significantly enhance care strategies.
Genetic studies aim to uncover underlying causes of gastroshiza. Understanding these risk factors may lead to preventive measures or targeted therapies in the future.
Additionally, multidisciplinary teams are increasingly common in treatment plans. Collaborations between surgeons, neonatologists, and geneticists ensure comprehensive care paths tailored to individual needs.
Clinical trials continue to test innovative treatments and approaches that could change how gastroshiza is managed from birth onward. Parents now have more hope than ever as research evolves rapidly in this field.
Support Resources for Families Affected by Gastroshiza
Families navigating the challenges of gastroshiza often find comfort and assistance through various support resources. Nonprofit organizations dedicated to congenital conditions provide valuable information and community connections.
Online forums can be a lifeline. Parents share experiences, tips, and emotional support in these virtual spaces. Engaging with others who understand the journey fosters a sense of belonging.
Local hospitals may offer family support groups as well. These gatherings allow families to meet face-to-face, sharing their stories and coping strategies in a safe environment.
Additionally, many healthcare providers have access to social workers specializing in pediatric care. They can help families navigate medical systems, financial aid programs, and emotional counseling options tailored for those dealing with gastroshiza.
These resources create networks that empower families during difficult times while promoting hope and resilience on the path ahead.
Conclusion
Gastroshiza is a complex condition that significantly impacts both the affected child and their family. Understanding this birth defect, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower parents and caregivers to navigate the challenges ahead. With advancements in medical research and increased support resources available, families are better equipped than ever to face these hurdles.
It’s essential for those impacted by gastroshiza to lean on community support and remain informed about the latest developments in care. Together, through knowledge sharing and empathetic understanding, we can foster hope for children with gastroshiza and enhance their quality of life as they grow. Whether you’re a parent or caregiver or simply someone looking to learn more about this condition, know that you’re not alone on this journey.